Horse owners may be wondering how horses see the world.
It’s interesting to know whether equines see the same as humans do.
So, do horses see in color? Yes, horses see in color but their vision is different from ours. Horses see colors but their color range is not as versatile as humans. Equine vision is dichromatic (two-color). This feature is taken into consideration while building obstacles for equestrian events. Horses have binocular and monocular types of vision.
Equines do see the world in other colors because of their unique sight.
Let’s trot on over equine vision and its sensitivity.
How Do Horses See?
Horse’s eyes are claimed as one of the biggest among land mammals. The eyes are placed laterally. This means they are placed on the sides of the equine’s head. This gives the animal a 350° vision, which is quite impressive. Such eye position is beneficial – originally it helped wild horses notice predators.
As for equine vision, there are two different types – binocular and monocular. Horses have 65° of binocular vision and 285° of monocular vision.

Horse Binocular Vision
Binocular vision means that an animal is able to spot the same direction with both eyes. This gives a better sense of distance and the steed can focus on the objects properly. Horses have a 3ft – 4ft blind spot just in front of them. Another blind spot is behind their head to the back and tail.
The horse raises its head when using binocular vision to see in the distance. It helps to focus on a distant object or a predator. If the equine needs to see an object near it, it keeps the head vertically and the neck is arched.
The range of vision can be “adjusted” by raising or lowering the head. With a raised head, the visual field is smaller. With a lowered head, the vision is better. You should mind these peculiarities when riding your companion and performing at horse shows.
When approaching the horse, it’s recommended to come from the side of the animal. As you don’t want to frighten your friend. Stay calm and wear protective gear like a helmet.

Horse Monocular Vision
Monocular vision allows an animal to use two eyes in different directions. There’s a vast array of equine monocular vision that gives a wide vision field. Equine’s perception of depth is not as good as humans.
Monocular vision greatly helps to notice an object or a predator coming from any direction. It’s good for spotting rapid movements in the distance. However, there are still blind spots even with this type of vision. The first one is right in front of the horses and the second one is behind them.
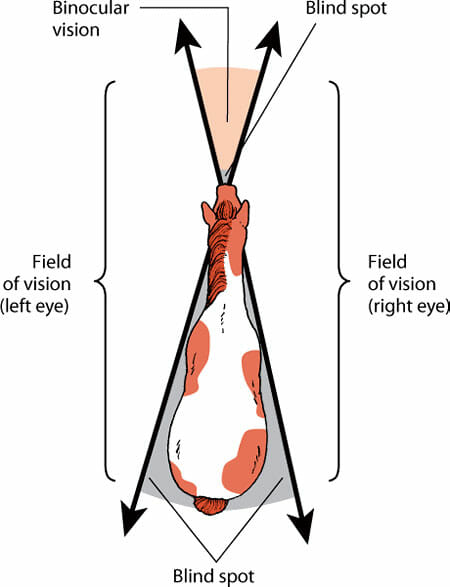
Equine Blind Spots
As horses have a few blind spots, we should be aware of them. These are the spots in front of and behind the equine. The area in front of the animal creates a triangle with its base at the eyes and a point at 3-4ft away. The blind spot behind the animal is a bit wider than the body width.
It’s crucial to know the horse’s blind spots to avoid standing in them for long. So it may seem to the animal that you appear and disappear from time to time. The steed can accidentally hit you because it didn’t see you. It could knock you over if you jump from nowhere in front of the face. The same goes for hind legs when standing at the back.
That’s why it’s important to know how to interact with a horse. You should come to it from its clear vision and stay in sight. The best way to approach is from the shoulder side. Speak to your companion while stepping up. And then you can touch the animal when it clearly sees you. Horses are not fans of surprises like rapid moves, jumps, hand waves, and loud noise.
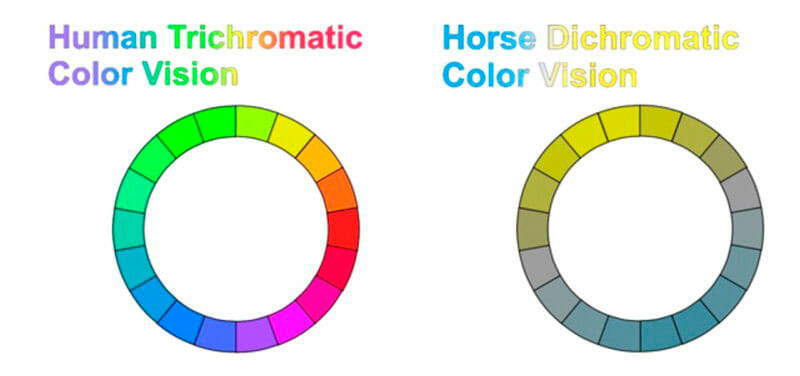
Color Vision
Horses have dichromatic vision, which means they have two types of receptors called cone cells. Whereas most humans have a trichromatic vision (three-color). So the animals differ colors in two wavelength areas of visible light.
Horses are able to distinguish between blue and green colors and their hues. But they can’t see the red color. That’s close to the vision of humans who are color-blinded.
In terms of equine anatomy, the animal has two types of cones in the eyes. That’s due to the horse’s behavior. They are more active at dawn and dusk when the rod cells come in handy.

Can Horses See in the Dark?
Yes, horses see in the dark. And they see even better than humans. The animals have excellent night vision because of the eye structure. There are special cells called rods in the equine’s eye that help them to see in the dark. And steeds have more rod cells than humans so they see at night better.
Horses also have better vision in dim conditions. They can still differ shapes in the low light. Equines are able to walk in the dark, unlike humans. On the contrary, horses can’t adjust to the rapid light changes quickly. Humans manage to do that better than these animals. For instance, when loading the horse into a trailer, give it some time to get used to the new conditions. Rapid light switching may affect the horse’s clear vision of the objects.

Horse Eye Disorders You Should Know About
Visit your vet regularly to check the horse’s eyes as well. Especially, in case you notice any redness or swelling. Avoiding proper treatment may lead to serious infection and blindness. The common eye disorders include corneal abrasion, keratitis, and conjunctivitis.

The Final Words About Equine Vision
Horses see in color and their vision is different from humans. They have binocular and monocular vision. This means the animals can use two eyes to look in the same direction or different. Such a vision helps to spot various objects in the distance and at hand.
There are blind spots that every equestrian should know about. Avoid standing in front of and behind the equine for too long. The horse may not notice you and hurt you by accident.
A horse’s eye has two types of cone cells that give the animal a dichromatic vision. Horses can distinguish between blue and green but they can’t see the red color. This aspect is taken into consideration when arranging the performing arena.
Horses have a brilliant night vision that allows them to move in low light conditions. Make sure your companion is safe when transferring him to another place. Put on horse boots to protect the limbs when traveling.
