
The horse is a mammal animal that is covered with thick fur, like cats and dogs. That’s why horse owners may be worried that their horses can get insects while spending time outdoors. So, do horses get fleas?
Horses can get fleas but it is a relatively rare case. Fleas are tiny wingless insects that consume the blood of their hosts. Unlike dogs or cats, equines have a much less dense coat. Thus, it is difficult for fleas to live and multiply on horses.
This article is a detailed guide on horse fleas. Let’s check where fleas usually spawn and what to do if your horse gets fleas.
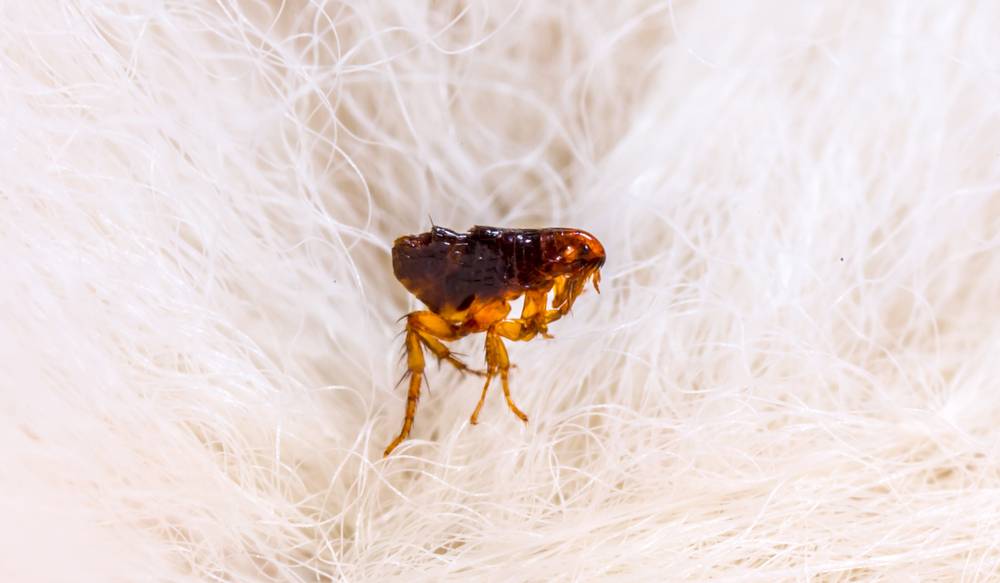

What Are Fleas and Why Are They Dangerous for Pets?
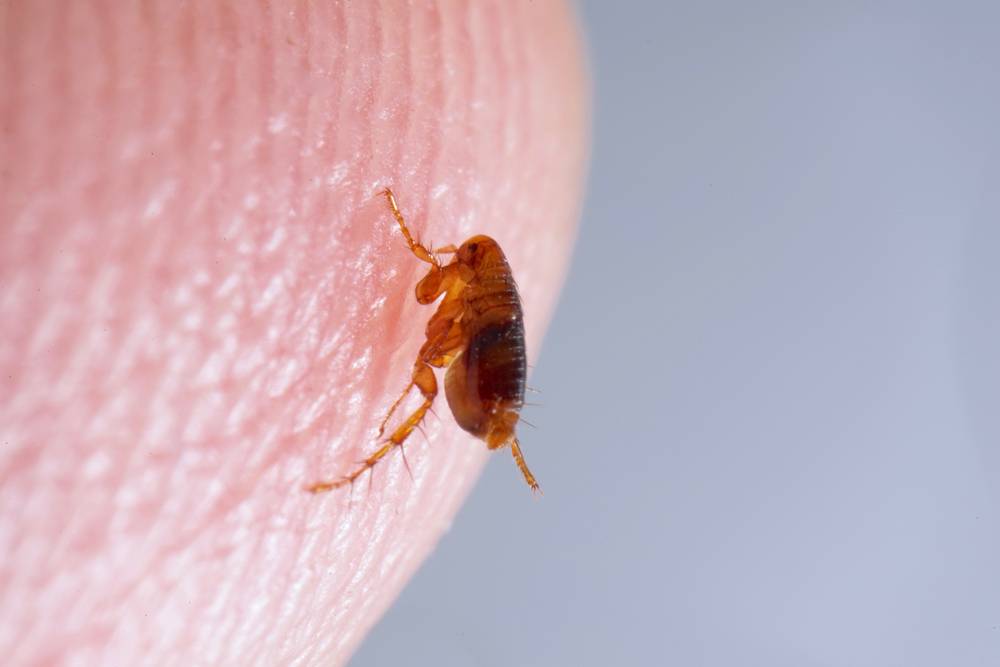
Fleas are small insects that commonly feed on the blood of their hosts. They are a typical parasite that can infest both animals and humans. They have a flattened body shape, which makes it easy for them to move through the hair of their host. Fleas are typically brown or black in color and can be as small as 1/16 of an inch in length. They have six legs and can jump up to 7 inches vertically and 13 inches horizontally. This makes the insects highly mobile and able to spread quickly from host to host.
Fleas are dangerous for pets because they can cause a variety of health problems. The most common one is skin irritation and scratching caused by an allergic reaction to the flea’s saliva. This can lead to hair loss, scabs, and even open sores on the pet’s skin. In addition, excessive scratching can also lead to secondary skin infections.
Parasites can also transmit diseases to pets like Lyme disease. Some species of fleas can carry the bacterial disease of murine typhus. The last may cause fever, headache, and muscle aches in pets and humans. They can also transmit tapeworms, which are intestinal parasites that can cause diarrhea and weight loss in animals.
In some cases, flea infestations can become so severe that they can cause anemia in pets. This occurs when a large number of fleas feed on the pet’s blood. This leads to a loss of red blood cells and a decrease in the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. Anemia can cause weakness, fatigue, and even death in severe cases.
The Life Cycle of Fleas
The life cycle of a flea is made up of four distinct stages: the egg, larva, pupa, and adult stages.
The egg stage is when adult female fleas lay eggs on their host. They usually pick a mammal such as a dog, cat, or horse. These eggs are tiny and white and can number up to 50-150 eggs per day. The eggs are not sticky, so they can easily fall off the host animal into the environment, such as carpet, bedding, or soil. The eggs usually hatch within 1-10 days, depending on the temperature and humidity.
The next stage is occurring the larva. Once the eggs hatch, they become tiny, worm-like larvae. These larvae feed on organic debris, such as flea feces, which contain digested blood, as well as other organic matter found in the environment. The larvae are typically found in areas where the host animal spends most of its time. The larvae stage lasts for about 5-11 days, depending on the environment.
The pupa stage is determined by the following. Once the larvae have finished feeding, they spin a cocoon around themselves and enter the pupal stage. The cocoon is made of a tough, silken material that protects the developing flea from its environment. The pupa stage lasts for about 5-14 days.
The adult stage is the final stage of the flea’s life cycle. Once the pupa is fully developed, the adult flea emerges from the cocoon and immediately begins to search for a host. Adult fleas can hide in dark places and live for several months. During that time, they will feed on the blood of their host and reproduce. Female fleas can lay up to 50-150 eggs per day, starting the cycle all over again.

How a Horse Can Get Fleas
Horses can get fleas in a few common scenarios, despite being less likely than other pets to get infested.
- If a horse comes into contact with another animal that is already infested with fleas, it can become infected as well. This can happen when the horse is stabled or boarded near an infested animal. Or when it comes into contact with an infected animal at a show or event. An equine may get fleas from other animals, as well as from another horse. Even though the parasites usually host specific species, sometimes dog fleas and cat fleas can bite a horse.
- Fleas thrive in warm and humid environments. If a horse lives in an area with high humidity, it may be at a higher risk of becoming infected.
- In case a horse’s living area is not kept clean and dry, it can get fleas. Fleas thrive in areas with piles of manure or other debris. You should keep the horse’s stall and bedding disinfected to prevent infestations.
- A poorly-groomed horse may be at a higher risk of getting fleas.
- If a horse strays from its usual environment, it may come into contact with insects in new areas. This could happen if the equine is taken on a trail ride through a wooded area, for example.

How to Get Rid of Horse Fleas
Treating horses with fleas requires a combination of environmental management, grooming, and the use of flea control products. Here are useful steps to follow when treating a horse with fleas:
- Clean and disinfect the horse’s shelter. This includes the stall, bedding, and any other areas where the horse spends time. Use a disinfectant or bleach solution to clean the area thoroughly. Remove any piles of manure or debris that could provide a breeding ground for fleas.
- Regular grooming of a horse can help to remove fleas from the horse’s coat and make it harder for them to survive. Use a flea comb to groom the animal and remove any flea eggs that may be present.
- There are several flea control products available for horses. These include flea shampoo, sprays, and powders. These repellent products can be applied directly to the horse’s skin and can help to kill adult fleas, their eggs, and larvae.
- Consult with your veterinarian before choosing any flea control products for your horse. The horse vet will be able to recommend the most suitable option based on your horse’s breed, age, and overall health condition.
- Flea control is an ongoing process, it is vital to repeat the tips mentioned above on a regular basis. This will help to prevent re-infestation.

Frequently Asked Questions
Where Fleas Can Be Found in the USA?
You can face fleas in any region all over the USA but these insects prefer a humid and warm place to live. One of the most common places where fleas can be found is in homes. Insects can easily find their way into homes through open doors and windows. They can also be brought in by pets. Once inside, fleas can quickly infest carpets and bedding, making it difficult to get rid of them.
Another common place is in outdoor areas, such as parks and wilderness areas. These spots provide a perfect environment for fleas to thrive. A high population of wild animals and plenty of organic debris are ideal feed for them. Fleas can also be found in areas where there is a high population of domestic animals, such as farms and stables.
Fleas can also be found in kennels, shelters, and pet stores. These places are known for having a large population of animals that can easily spread fleas. Insects can also be found in overcrowded areas such as parks, playgrounds, and beaches.
How to Prevent Horse Fleas?
One of the most efficient ways to prevent fleas is to maintain a clean living environment for the horse. This includes regularly cleaning and disinfecting the horse’s stall, bedding, and any other horse-related areas.
Proper grooming is another essential aspect to eliminate fleas. Grooming the horse can help to get rid of fleas from the horse’s coat. Regular bathing with soapy water can also be helpful in removing fleas or mites from the horse’s fur.
Using flea control products is another preventional option. Choose an item that kills fleas and is specially designed for horses.
Why Do Horses Get Fleas Rarely?
The horse’s skin is much thicker and less sensitive than that of dogs or cats. This makes it harder for fleas to bite through the equine’s skin. This also makes it harder for insects to survive once they do.
In addition, horses are known to groom themselves frequently. This routine can help remove any fleas that may have made it onto their coat. Equines also have natural immunity against certain types of insects, which makes them less susceptible to a flea infestation.
Conclusion
Staying aware of fleas is important in preventing infestation even if it is a rare case. Horse owners should be aware of the common signs and measures to take. If you suspect your horse got fleas, it’s vital to take action quickly to prevent further discomfort for your companion.
